Consolidation of soil
Consolidation is the process in which reduction in volume takes place by expulsion of water under long-term static loads. When stress is applied to a soil that causes the soil particles to pack together more tightly. When this occurs in a soil that is saturated with water, water will be squeezed out of the soil. Various theories have been proposed in the literature to predict the consolidation of soil. This includes Terzaghi’s consolidation theory (1943) and Mikasa’s finite strain consolidation theory (1963). The civil engineering lab in Kunsan National University can predict the consolidation of soil using these two theories.
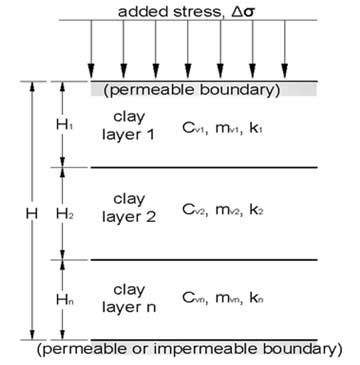 Consolidation in layered clay soil under added stress
Consolidation in layered clay soil under added stress
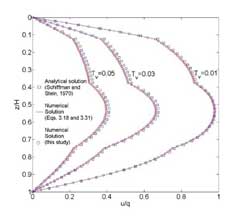 Excess pore water pressure isochrones
Excess pore water pressure isochrones
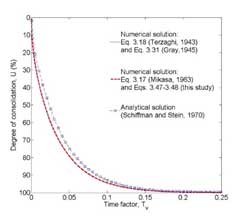 Time factor (Tv) vs degree of consolidation (U)
Time factor (Tv) vs degree of consolidation (U)