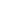
Geotextile tube application
The traditional practice of constructing shoreline protection, involves the use of conventional materials, such as rocks, aggregate, and concrete. Due to the rising capital and maintenance cost of traditional systems, depletion of natural rock, and environmental concerns, there is a growing interest in low cost novel systems. Recently, geotextile tube technology has been gaining popularity since it is an environmentally friendly solution with low carbon dioxide emission. Geotextile tubes have been applied in Saemangeum as temporary dikes to create a 3.0 km long artificial land that would help facilitate in the construction of the foundation of a 2.0 km long bridge. Utilizing geotextile tubes in the project prevented the erosion of the backfill soil during flooding, and resulted in significant cost savings.
 Geotextile tube technology applied in Saemangeum
Geotextile tube technology applied in Saemangeum
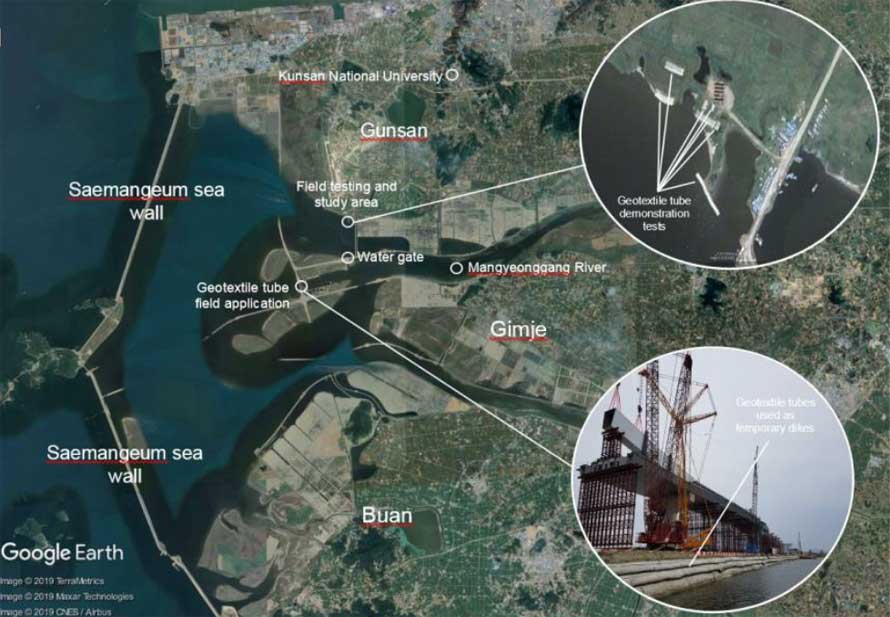
 Conventional method of constructing embankment
Conventional method of constructing embankment
 Embankment constructed using geotextile tubes
Embankment constructed using geotextile tubes
Modified geotextile tube
The performance of geotextile tubes is affected by many factors such as the pumping pressure, fill material and geotextile properties, etc. Hence, obtaining hydraulic compatibility between geotextiles and fill materials containing a variety of coarse and fine particles, i.e. silty sand, is complex. For this reason, the modified geotextile tube (MGT) was invented to optimize the filling and dewatering or consolidation performance of geotextile tubes.
 Modified geotextile tube: a) MGT miniature composed of woven PP and woven PET at the bottom and top, respectively and b) MGT behavior or mechanism
Modified geotextile tube: a) MGT miniature composed of woven PP and woven PET at the bottom and top, respectively and b) MGT behavior or mechanism
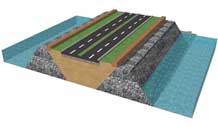
 Analytical model of modified geotextile tube
Analytical model of modified geotextile tube